One to one maths interventions built for KS4 success
Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons now available
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Arithmetic Converting units of time Converting metric units Conversion of unitsThis topic is relevant for:

Formula For Speed
Here we will learn about the formula for speed including understanding and using the terms constant speed and average speed. We will also be calculating the average speed of an object given its distance and time. This will extend to using and applying the speed formula and solving problems involving the formula for speed.
There are also worksheets on the formula for speed distance and time based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What is the formula for speed?
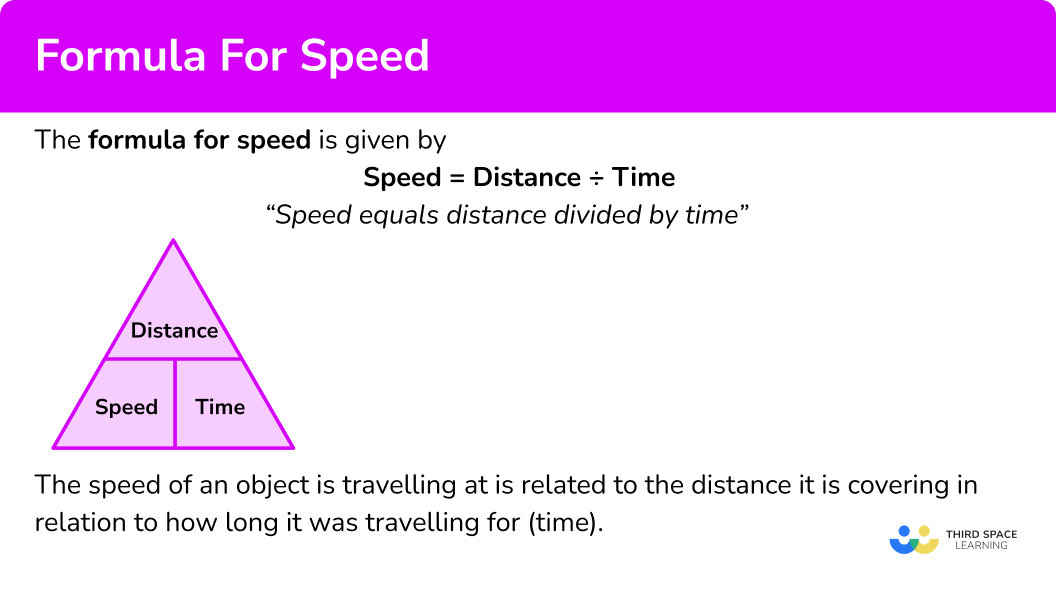
The formula for speed is given by
Speed distance time
“Speed equals distance divided by time”
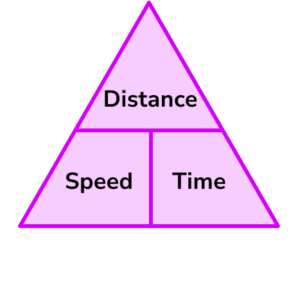
You will normally shorten this to the below:
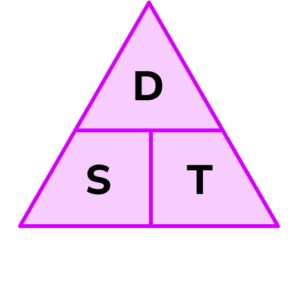
The speed of an object is travelling at is related to the distance it is covering in relation to how long it was travelling for (time).
What is the formula for speed?
What is speed?
Speed is about how fast an object moves. The speed of the moving object is found by calculating the relationship between the distance the object travels and the period of time taken to travel the distance.
Some examples of the units of speed are:
- Metres per second
- Miles per hour
- per hour
- Speed of sound metres per second
- Speed of light metres per second
Constant speed is where the speed does not change, e.g. a straight line on a distance-time graph indicates a constant speed.
We can calculate the average speed of an object by dividing the total distance by the total time.
If you also consider the direction of the movement as well at its speed then this is called the object’s velocity.
What is time?
Time can be defined as the ongoing sequence of events taking place.
Some examples of the units of time are:
- Seconds
- Minutes
- Hours
- Days
Note: The unit (Standard Unit Measurement) for time is a second.
What is distance?
Distance is the length of space between two points.
Some examples of the units of distance are:
- Millimetres
- Centimetres
- Metres
- Kilometres
- Miles
Note: if we only consider how far the object has moved in regards to its starting point this is called displacement.
Rate of change
The speed of an object is the rate of change between the distance covered and the amount of time taken. When working with graphs the rate of change can be found by calculating the gradient of the distance-time graph.
This page focused specifically on speed. If you want to focus on speed, distance, time please follow the link below.
Step-by-step guide: Speed distance time (coming soon)
How to use the formula for speed
In order to use the formula for speed:
- Write down which variable you know with their units.
- Check the units align, do any need to be converted?
- Write down the formula for speed.
- Solve to find speed (or distance or time).
- Clearly state your answer with the correct units.
Explain how to use the formula for speed

Speed distance time worksheet

Get your free speed distance time worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Speed distance time worksheet

Get your free speed distance time worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREERelated lessons on compound measures
Formula for speed is part of our series of lessons to support revision on compound measures. You may find it helpful to start with the main compound measures lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Formula for speed examples
Example 1: calculating speed by substituting values into the speed formula
Question: A car travels at a constant speed. The train travels in
Give your answer in miles per hour
- Write down which variable you know with their units.
Speed: unknown
Distance:
Time:
2Check the units align, do any need to be converted?
Units are correct as the questions’ units are already in miles and hours.
3Write down the formula for speed.
4Solve to find speed (or distance or time).
We are finding the speed.
5Clearly state your answer with the correct units.
The car travels at
Example 2: calculating speed by substituting values into the speed formula
Question: A train travels at a constant speed. The train travels a total distance of in a period of time of
Give your answer in kilometre per hour
Write down which variable you know with their units.
Speed: unknown
Distance:
Time:
Check the units align, do any need to be converted?
Units are correct as the questions’ units are already in kilometres and hours.
Write down the formula for speed.
Solve to find speed (or distance or time).
We are finding the speed.
Clearly state your answer with the correct units.
The car travels at
Example 3: calculating speed by substituting values into the speed formula with unit conversion
Question: A person walks at a constant speed. They travel in
Give your answer in metres per minute
Write down which variable you know with their units.
Speed: unknown
Distance:
Time:
Check the units align, do any need to be converted?
The answer is asked to be given metres per minute.
The distance is already given in metres so you do not need to convert this unit.
The time is given in hours so you need to convert this to minutes.
Speed: unknown
Distance:
Time:
Write down the formula for speed.
Solve to find speed (or distance or time).
We are finding the speed.
Clearly state your answer with the correct units.
The car travels at
Example 4: using speed to find another value
Question: Phil is in a running race. Phil runs at an average speed of
The race is long.
What is the amount of time Phil takes to finish the race?
Give your answer in and
Write down which variable you know with their units.
Speed:
Distance:
Time: unknown
Check the units align, do any need to be converted?
The question used two different units of distance, you need to convert one so you are working with equivalent distances. In this question it is easier to convert to
Because you now have equivalent units of distances you can calculate Phil’s time before converting to and
Write down the formula for speed.
Solve to find speed (or distance or time).
We are finding the time. We need to adapt the speed formula.
Clearly state your answer with the correct units.
You have calculated the time to be
However the question wants the time in and
Remember:
Therefore
and
Therefore
Phil completes the race in and
Example 5: using speed to find another value
Question: A train travels at for Calculate the total distance travelled.
Write down which variable you know with their units.
Speed:
Distance: unknown
Time:
Check the units align, do any need to be converted?
The units align. Sometime people prefer decimals to fractions, so we can use or
Write down the formula for speed.
Solve to find speed (or distance or time).
We are finding the time. We need to adapt the speed formula.
Clearly state your answer with the correct units.
You have calculated the time to be
Therefore the distance of the journey is
Example 6: problem involving speed
Miss Yellow completes a journey in stages.
In the first stage she travels at in
In the second stage she travels in and
The final stage is much shorter and she travels in
What was her average speed for the whole journey?
Give your answer in to significant figures.
Write down which variable you know with their units.
You want to know Miss Yellow’s overall average speed so you need to calculate her total distance and total time
Speed: unknown
Distance:
Time: and
Check the units align, do any need to be converted?
You will notice in the above the units are not the same for distance or speed. You need to convert them all first before proceeding.
Distance: convert all to
Therefore total distance is
Time: convert all to
and
Therefore total time is
Write down the formula for speed.
Solve to find speed (or distance or time).
Clearly state your answer with the correct units.
needs to be rounded to significant figures
The car travels at
Common misconceptions
- Incorrect formula for speed
You must remember the speed formula with the correct operations between distance and time.
- Units
You must remember the relationship between the units is important for the context of the question. If you are given an object’s speed in km per hour and the time as minutes you need to first convert one of the units to be able to give an answer in hours.
E.g. does not give you
- Check if you answer is ‘sensible’
If you have found the speed of a car is you have most likely made an error as this answer is not ‘sensible’ within the context of the question as it is too high speed for a car. This is a useful (and quick) way of checking your answer.
Practice formula for speed questions
1. Find the speed of an object which travelled in Give your answer in




2. Find the speed of an object which travelled in Give your answer in




3. Find the speed of an object which travelled in Give your answer in




4. A person walks at a constant speed. They travel in Calculate the speed. Give your answer in metres per minute




5. A person walks at a constant speed of miles per hour. They walk for Calculate how far they walk.




6. An object travels at a speed of Calculate the time taken. Give you anwer in




is
Formula for speed GCSE questions
1. Emily drives her car in What is her average speed?
(2 marks)
(1)
(1)
2. Jenny left her home at and walked to the library. She arrived at The library is from her house.
(a) What was Jenny’s average speed?
(b) On the return journey she takes a longer route home which is longer than before. She takes to walk home.
On which journey was Jenny walking faster?
You must show your workings.
(5 marks)
(a)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(b)
(1)
Faster walking to the library
(1)
3. Seobin was driving to a hotel.
He looked at his Sat Nav at it said he had left for his journey.
Seobin arrived at the hotel at
Work out his average speed between and
(4 marks)
Attempt to find the time taken for the journey
(1)
or
(1)
(1)
(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- Use compound units such as speed
- Solve simple kinematic problem involving distance and speed
- Change freely between related standard units (eg time, length) and compound units (e.g. speed) in numerical contexts
- Work with compound units in a numerical context
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.
Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.