High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Fractions Decimals Percent Converting fractions decimals and percentagesHow to find probability
Here you will learn about how to find probability, including how to find probability using words, recognising the likelihood of an event and placing events on a probability scale.
Students will first learn about how to find probability as part of statistics and probability in th grade.
What is how to find probability?
Finding probability is when you make judgements as to whether an event will take place. To do this, you describe how probable the event is.
For example,
You may say that it is likely to rain tomorrow, or that it is impossible for the sun not to rise.
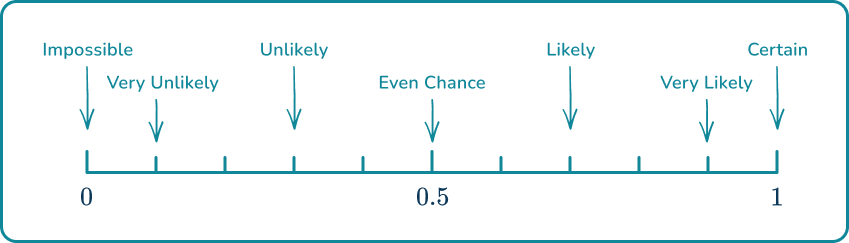
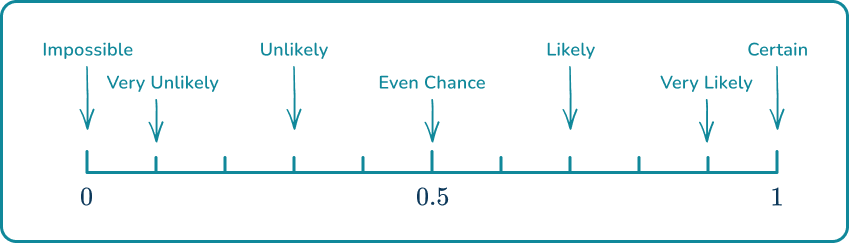
Some other common words used to describe the probability of an event happening include; certain, very likely, even chance, unlikely and very unlikely.
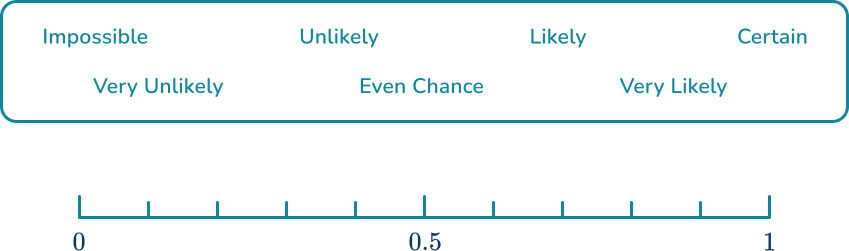
These words can be placed on a probability scale starting at (impossible) and ending at (certain).
![[FREE] Probability Worksheet (Grade 7 to 12)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Probability-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Probability Worksheet (Grade 7 to 12)
![[FREE] Probability Worksheet (Grade 7 to 12)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Probability-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 7 to 12 students’ understanding of probability. 15+ questions with answers covering a range of 7th to 12th grade probability topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Probability Worksheet (Grade 7 to 12)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Probability-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Probability Worksheet (Grade 7 to 12)
![[FREE] Probability Worksheet (Grade 7 to 12)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Probability-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 7 to 12 students’ understanding of probability. 15+ questions with answers covering a range of 7th to 12th grade probability topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEProbability scale
The probability scale is used to represent probabilities on a number line from (impossible) to (certain).
Events that are neither impossible nor certain, can be placed somewhere on a probability scale. To do this, you need to consider the words suitable to describe the probability of the event happening, or the number which would represent the chance of the event happening.
For example,
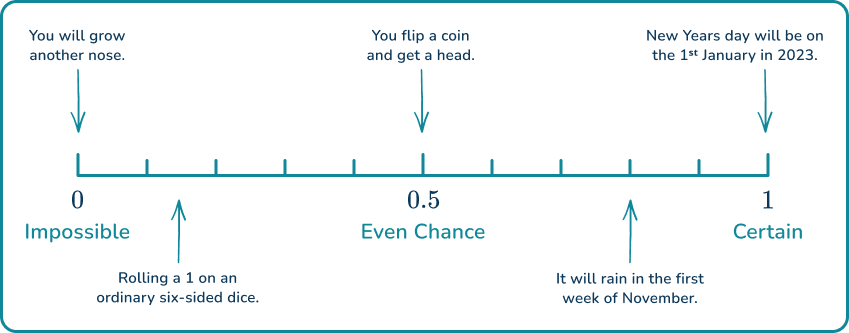
Step-by-step guide: Probability scale
The probability of an event happening can be calculated using the formula
For example,
Let’s calculate the probability of getting an odd number when a fair die is rolled.
The desired outcome is rolling an odd number. There are odd numbers on the die.
The total number of possible outcomes is since there are numbers on the die.
The probability of getting an odd number
Step-by-step guide: How to calculate probability
What is how to find probability?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to th grade math?
- Grade 7 – Statistics and Probability (7.SP.C.5)
Understand that the probability of a chance event is a number between and that expresses the likelihood of the event occurring. Larger numbers indicate greater likelihood.
A probability near indicates an unlikely event, a probability around indicates an event that is neither unlikely nor likely, and a probability near indicates a likely event.
- Grade 7 – Statistics and Probability (7.SP.C.7)
Develop a probability model and use it to find probabilities of events. Compare probabilities from a model to observed frequencies; if the agreement is not good, explain possible sources of the discrepancy.
How to describe probability in words
In order to describe probability in words:
- Consider the likeliness of the event happening.
- Choose an appropriate word from the list to describe the probability.
How to find probability in words examples
Example 1: how to find probability in words
Describe the likelihood that a number will be scored when an ordinary six-sided dice is rolled once.

- Consider the likeliness of the event happening.
An ordinary six-sided dice will have the numbers to on its faces. Scoring a on an ordinary six-sided dice will definitely not happen.
2Choose an appropriate word from the list to describe the probability.
Scoring a on an ordinary six-sided dice cannot happen.
It is impossible to score a on an ordinary six-sided dice.
Example 2: how to find probability in words
In words, describe the probability that a red counter is obtained when a counter is taken at random from a bag that contains red counters and blue counters.
Consider the likeliness of the event happening.
A red counter being obtained from the bag could happen, the bag does contain red counters, so you cannot describe it as impossible.
You could get a red or a blue counter out of the bag, so you cannot describe the probability of getting a red counter as certain.
The chance of getting a red counter out of the bag is higher than blue. There are more red counters than blue in the bag. So you cannot describe it as unlikely, or even chance.
You can say it is likely or very likely that we would obtain a red counter from the bag.
Choose an appropriate word from the list to describe the probability.
In this instance, the chance of getting a red counter from the bag is much higher than blue.
It is very likely we would obtain a red counter from the bag.
How to place events on a probability scale
In order to place events on a probability scale:
- Consider the mathematical likeliness of the event happening.
- Choose the appropriate place on the scale to place the event.
Placing events on a probability scale examples
Example 3: placing events on a probability scale
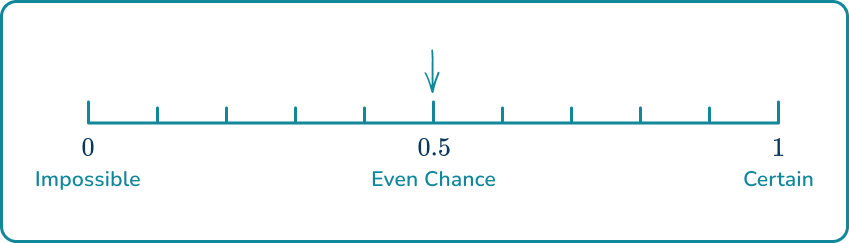
Mark on the scale below, the probability that an ordinary six-sided dice is rolled and lands on an even number.

Consider the mathematical likeliness of the event happening.
An ordinary six-sided dice will have the numbers to on its faces. Rolling an even number could happen, so you cannot describe it as impossible.
You could also roll an odd number on an ordinary six-sided dice, so you cannot describe it as certain.
There are odd numbers and even numbers on an ordinary six-sided dice. Two possible outcomes, odd or even, both with a chance.
Choose the appropriate place on the scale to place the event.
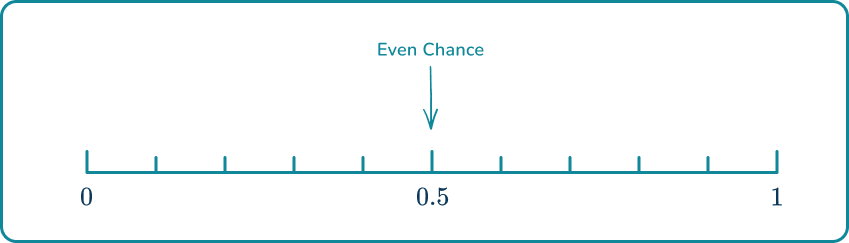
Two equally likely possible outcomes mean that there is an even chance that an even number is rolled, so make a mark halfway between (impossible) and (certain), at (even chance).
Example 4: placing events on a probability scale
There are marbles in a bag.
marbles are yellow.
marbles are green.
marbles are red.
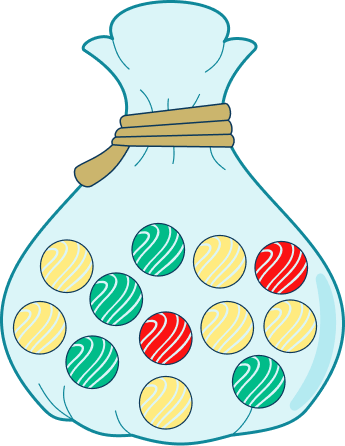
The probability that Lucas randomly chooses a red marble is or
On the probability scale, mark the probability.

Consider the mathematical likeliness of the event happening.
The mathematical probability is given.
Choose the appropriate place on the scale to place the event.
Visualize where would fall on the number line.

How to find probability
In order to find probability:
- Identify the sample space.
- Write out the basic probability as a ratio.
How to find probability examples
Example 5: basic probability of a single event
Jamie has the following cards:

A card is chosen at random. Find the probability the card has a letter on it.
Identify the sample space.
All possible outcomes are and and each card has an equally likely chance of being chosen.
Note: Because cards and repeat, their total probability is higher.
Write out the basic probability as a ratio.
The number of cards with is and the total number of cards is
Example 6: probability example of multiple events
Hussain rolls a fair dice and flips a fair coin. What is the probability that the dice lands on and the coin lands on tails?
Identify the sample space.
Let’s model with a table.
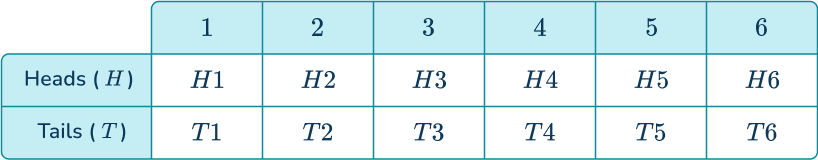
All possible outcomes are shown in the list and each number on the dice has an equally likely chance of being chosen and each side of the coin has an equally likely chance of being chosen.
Write out the basic probability as a ratio.
Tails and only appear once together in the table, so the number of favorable outcomes is The number of total possible outcomes is
Teaching tips for how to find probability
- When introducing finding probability, start with simple events before moving on to multiple events. Provide many opportunities for students to conduct their own experiments (flipping coins, rolling dice, etc.).
This allows students to create relative frequency tables and graphs and make sense of them. Also, encourage students to represent the sample space in an increasingly efficient way.
- Give students who need extra support access to a probability calculator to check their work.
Easy mistakes to make
- Forgetting the probability scale goes from (impossible) to (certain)
Remember that impossible is at and certain is at when probability scales are marked numerically rather than with words.
For example,
- Not understanding even chance
An event can only be described as having an “even chance” of occurring if the number of times it could occur is exactly the same as the other possible outcome.
For example,
When flipping a coin, a coin only has two sides. One contains heads and the other tails. So the coin landing on heads and the coin landing on tails has an equal chance of happening.
- Not understanding unfair events
Just because an event has two outcomes, it does not mean that the two events have equal probabilities.
For example,
A cube has six faces. One face is red and the other faces are blue. There are outcomes: red and blue. But the probabilities are different.
The probability of getting red is and the probability of getting blue is
Related probability lessons
- Probability
- Probability notation
- Probability formula
- Independent events
- Mutually exclusive events
- Tree diagram probability
- Conditional probability
- Venn diagram
Practice how to find probability questions
1. Place the words in the box onto the probability scale.

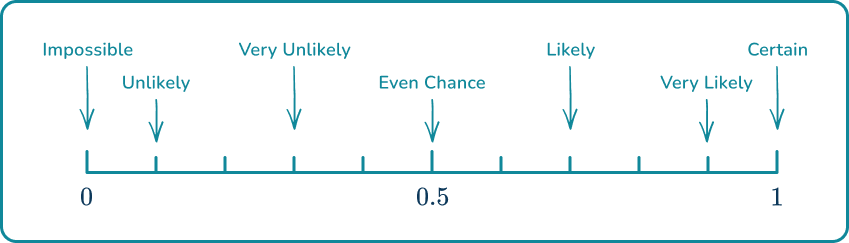

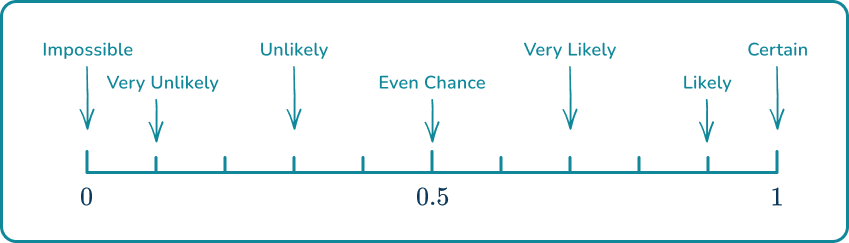

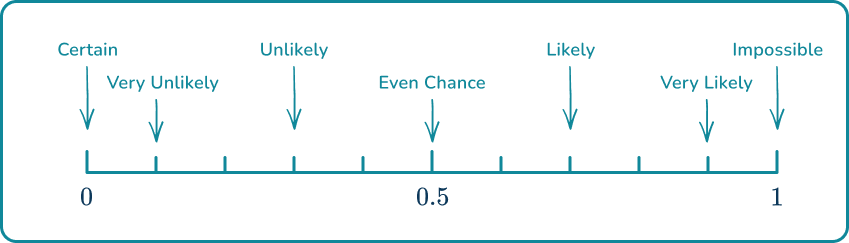

Remember that impossible is at and certain is at when probability scales are marked numerically rather than with words.
For example,

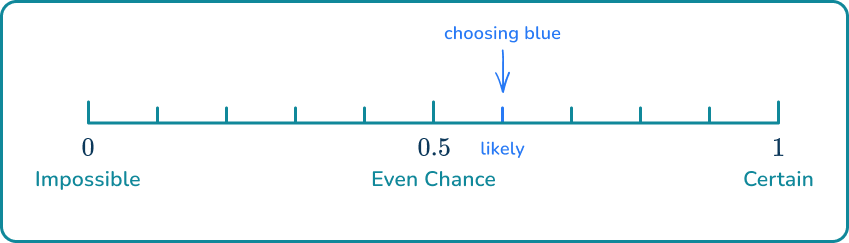
2. Use a word from the box to describe the probability that a blue marble is picked from the bag below.

Impossible

Unlikely

Certain

Likely

There are blue marbles and that are not blue. This means the probability is slightly greater than so it is a likely event.
3. Use a word from the box to describe the probability that a red marble is picked from the bag below.

Unlikely

Impossible

Very Unlikely

Likely

There are no red counters in the bag, so a red counter cannot be picked. The probability is
4. The probability that a green marble is picked from the bag below is Show where this belongs on the probability scale.



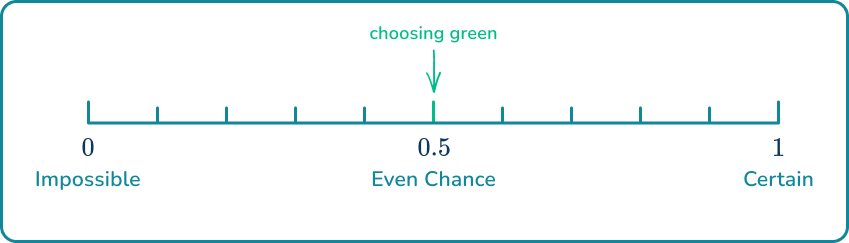




The blue number line below shows fifths.

or is close to so it is unlikely.
5. Alyssandra uses some letter cards to spell out her name.
![]()
She takes one of these cards at random.
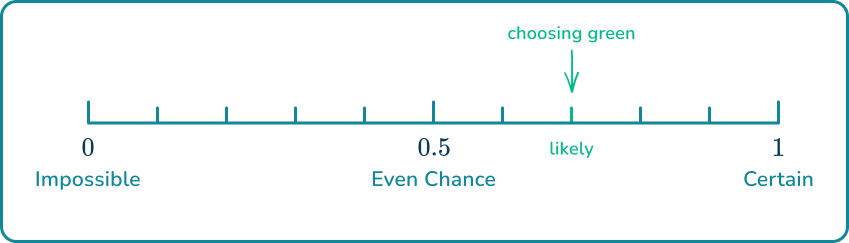
Mark on the scale below, the probability that Alyssandra takes a card containing the letter







The total number of outcomes is because of the different cards. The desired outcome is the letter which is on cards.
So the probability as a ratio is to or which is also equal to as a decimal. This falls between and on the probability scale, making it an unlikely event.
6. Maria flips a fair coin and chooses a marble from the bag. What is the probability that the coin lands on heads and the marble is blue?





Let’s model with a table.
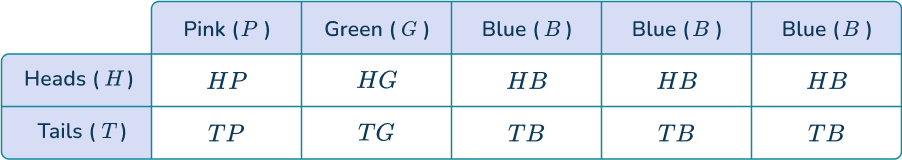
Heads and blue appear times together in the table, so the number of favorable outcomes is The number of total possible outcomes is
How to find probability FAQs
The use of math to calculate the probability in theory.
An event that is affected by the outcome of the first event.
It means it has at least one favorable outcome.
To understand the probability of an unknown structure, you must use statistics. This can include but is not limited to, using the normal distribution, standard deviation, confidence intervals, -scores, -tables and other advanced statistical processes and theorems.
The next lessons are
- Compound events
- Probability distribution
- Units of measurement
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!